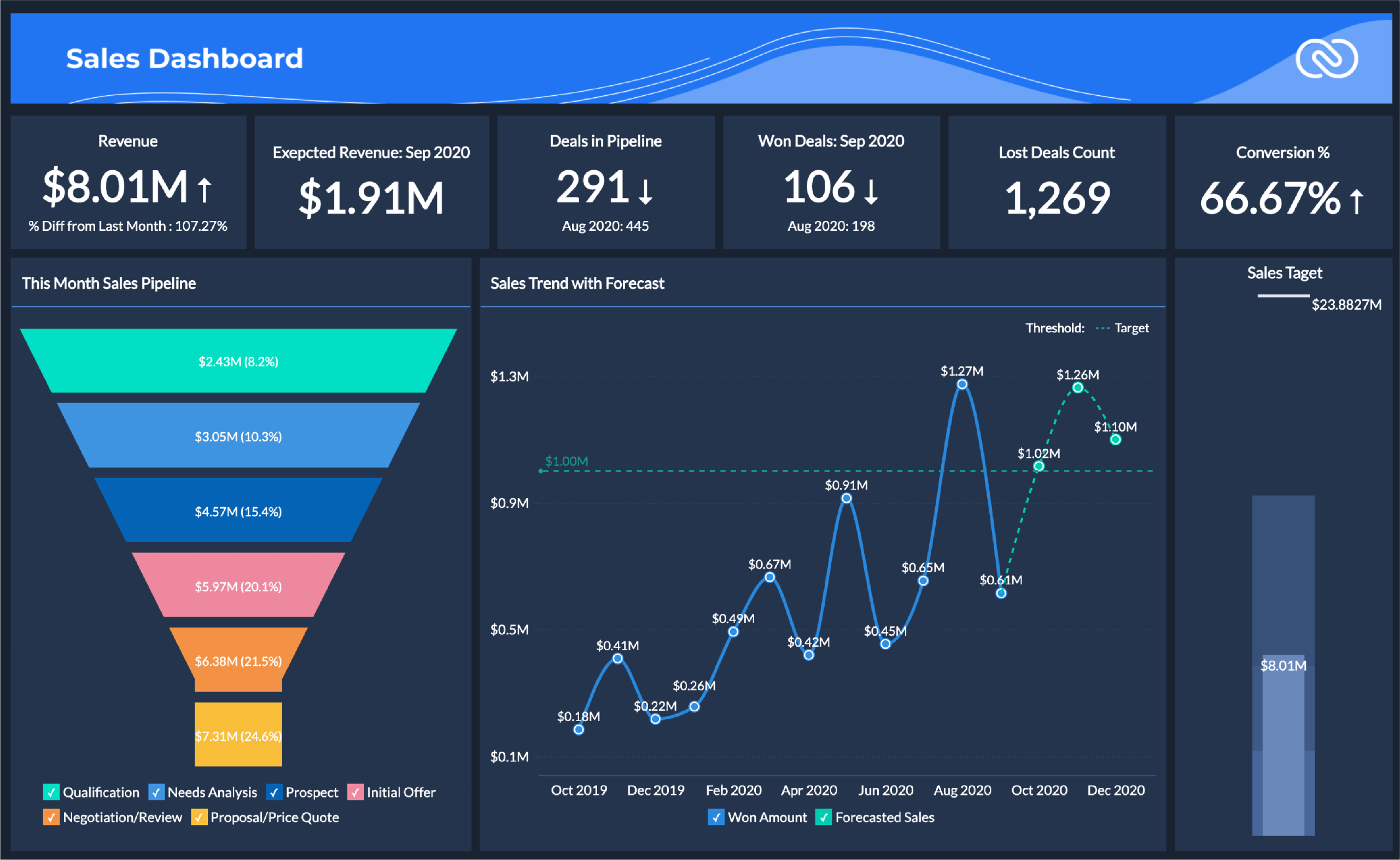
crm analytics examples open the door to a deeper understanding of how businesses harness customer data to drive smarter decisions and creative solutions. Imagine uncovering patterns in customer behavior, predicting future trends, and seamlessly boosting sales—all beginning with the power of CRM analytics.
By exploring practical crm analytics examples, you’ll see how organizations segment customers, score leads, and forecast sales with laser precision. CRM analytics leverages data from interactions, transactions, and engagement, transforming them into actionable insights that enhance customer relationships and optimize performance across industries.
Introduction to CRM Analytics
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) analytics refers to the use of data analysis tools and strategies to gain actionable insights from customer interactions, behaviors, and preferences. In today’s fast-paced digital economy, CRM analytics has become a vital component for organizations striving to strengthen customer relationships, fine-tune business strategies, and stay competitive. By leveraging CRM analytics, companies can make informed decisions that directly impact customer satisfaction and business growth.
The core objectives of CRM analytics revolve around understanding the customer journey, optimizing touchpoints, and personalizing experiences. Businesses employ CRM analytics to predict customer needs, improve service delivery, and identify high-value opportunities, thereby maximizing customer lifetime value and retention rates.
Data is central to CRM analytics. Common data sources include customer purchase histories, communication logs, website interactions, support tickets, and social media engagement. This rich pool of structured and unstructured data enables businesses to uncover hidden patterns and trends that would otherwise go unnoticed.
Common Use Cases of CRM Analytics: Crm Analytics Examples

CRM analytics finds application in a wide variety of business scenarios, helping organizations streamline processes and enhance customer-centricity. The following points Artikel its most common use cases and real-world impact.
Organizations utilize CRM analytics to address key business needs and drive operational improvement. By analyzing customer data, companies can tailor marketing efforts, manage sales pipelines more efficiently, and anticipate market demand. Here are typical scenarios where CRM analytics delivers measurable results:
- Customer segmentation for targeted marketing campaigns
- Lead scoring to prioritize sales efforts on high-potential prospects
- Sales forecasting for accurate revenue prediction
- Churn analysis to reduce customer attrition rates
- Personalized offer recommendations to boost conversion rates
- Campaign performance analysis for continuous improvement
For example, in the retail industry, CRM analytics helps brands segment customers based on buying habits, enabling more effective promotions. In B2B companies, lead scoring models empower sales teams to focus on the most promising opportunities, while financial services firms utilize churn analysis to proactively engage clients at risk of leaving.
CRM Analytics Metrics and KPIs
Measuring the effectiveness of CRM strategies involves tracking key metrics and KPIs. These indicators provide a clear picture of customer engagement, sales performance, and service quality. Businesses rely on these metrics to set benchmarks, monitor progress, and guide strategic adjustments.
| Metric | Description | Usage Example | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) | The predicted net profit attributed to the entire future relationship with a customer. | Segmenting customers by CLV to prioritize retention strategies. | Helps allocate resources to high-value customer segments. |
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | The cost associated with acquiring a new customer, including marketing and sales expenses. | Comparing CAC to CLV to assess marketing ROI. | Ensures sustainable customer growth and profitability. |
| Churn Rate | The percentage of customers lost over a specific period. | Identifying spikes in churn after service changes. | Drives retention strategies and product development. |
| Net Promoter Score (NPS) | A measure of customer loyalty and satisfaction based on survey responses. | Tracking NPS before and after a new feature launch. | Guides improvements in customer experience and advocacy. |
By closely monitoring these metrics, businesses can interpret trends, identify problem areas, and generate actionable insights. For example, a sudden increase in churn rate may prompt a review of recent policy changes, while a rising CLV in a particular segment could signal an opportunity to expand targeted offers.
Examples of CRM Analytics in Action
The practical application of CRM analytics spans multiple sectors, with organizations harnessing data-driven insights to achieve specific objectives. The following points highlight real-world implementations and outcomes, showcasing the diversity and effectiveness of CRM analytics.
- Retail: A global apparel company uses purchase and browsing data to create micro-segments, resulting in more relevant product recommendations and a 20% increase in average order value.
- Finance: A leading bank leverages predictive analytics to identify customers likely to apply for loans, optimizing targeted outreach and increasing conversion rates by 15%.
- Healthcare: A hospital network utilizes CRM analytics to personalize patient engagement, improving follow-up appointment rates and patient satisfaction scores.
Data collection methods in these cases typically involve CRM system logs, integration with e-commerce platforms, transaction databases, and survey responses. Analytical approaches range from descriptive statistics to advanced machine learning models, transforming raw data into strategic value.
CRM Analytics Techniques and Methods
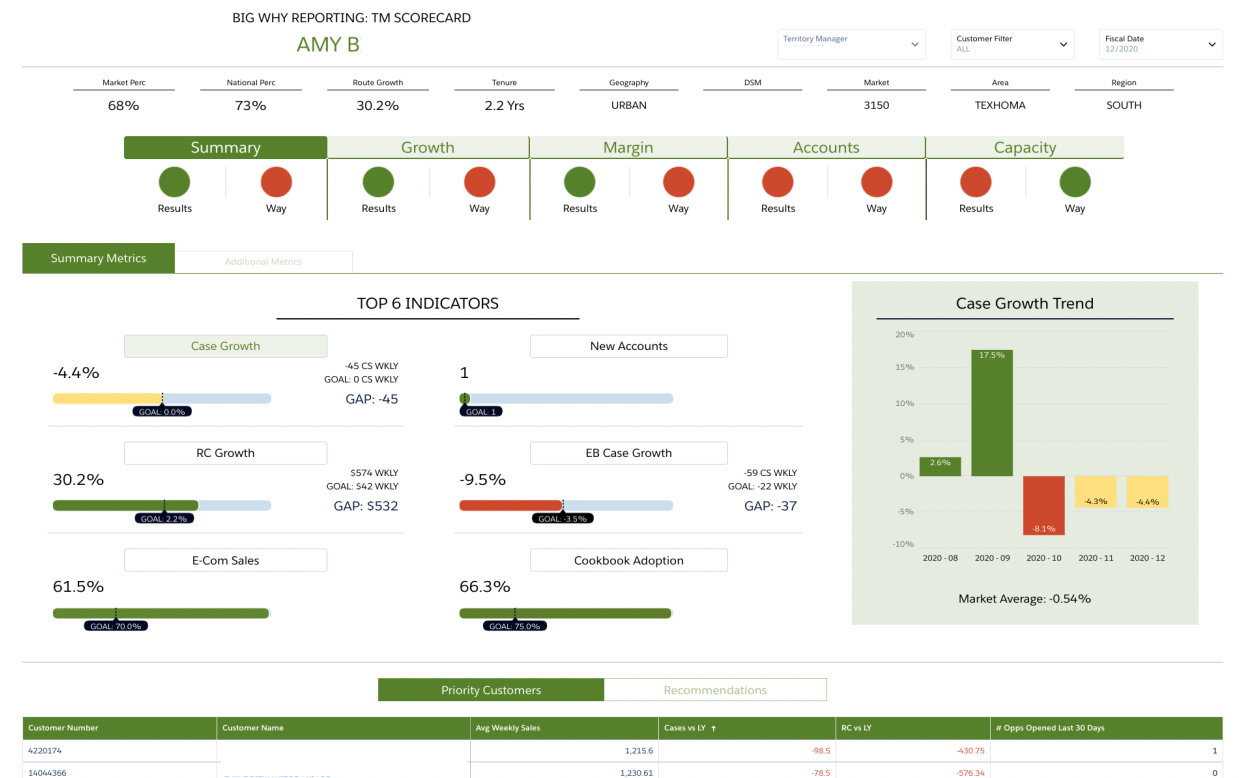
Several analytical methods underpin CRM analytics, each serving different objectives from prediction to segmentation. Choosing the right technique is crucial for maximizing insight and business impact. Below is an overview of common techniques and their applications, organized in table format for clarity.
| Technique | Description | Application | Tools Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictive Modeling | Uses historical data to forecast future customer behaviors or outcomes. | Forecasting customer churn, sales, or product demand. | Python (scikit-learn), R, IBM SPSS |
| Cluster Analysis | Groups customers into segments based on shared characteristics or behaviors. | Creating targeted marketing campaigns for different customer groups. | Tableau, SAS, K-means algorithms |
| Customer Lifetime Value Calculation | Estimates the total value a customer brings over their relationship with the company. | Prioritizing high-value customers for retention efforts. | Excel, SQL, CRM software analytics modules |
| Sentiment Analysis | Analyzes customer feedback to gauge sentiment and satisfaction. | Monitoring brand perception on social media and support channels. | Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK), Brandwatch |
While predictive modeling excels in forecasting outcomes and optimizing resource allocation, cluster analysis is particularly effective for identifying market segments and personalizing offers. Sentiment analysis provides unfiltered insights into customer perceptions, and customer lifetime value calculations guide long-term strategy and investment.
Visualizing CRM Analytics Data
Data visualization transforms complex CRM analytics into clear, actionable narratives. By representing trends, patterns, and outliers visually, organizations can grasp insights quickly and communicate findings across teams. Visualization tools not only enhance data interpretation but also foster a culture of data-driven decision-making.
Common data visualization formats in CRM analytics include:
- Dashboards: Integrated interfaces displaying real-time KPIs, sales funnels, and customer engagement metrics for holistic monitoring.
- Charts: Bar, line, and pie charts depict trends such as sales growth, segmentation, or campaign performance over time.
- Heatmaps: Visual representations of customer interactions on web pages or email campaigns, highlighting areas of high engagement.
For instance, a dashboard might reveal declining engagement in a specific customer segment, prompting targeted action. Heatmaps can illustrate which product categories receive the most attention, guiding inventory and promotional strategies. Charts help track the effectiveness of marketing initiatives, enabling iterative improvements.
Integrating CRM Analytics with Other Business Systems
Connecting CRM analytics with marketing automation, enterprise resource planning (ERP), and support systems creates a unified ecosystem for data management and operational efficiency. Integration breaks down data silos, enabling cross-functional insights and streamlined workflows.
Businesses typically integrate CRM analytics with other systems via APIs, middleware platforms, or built-in connectors. This enables automatic data sharing, reduces manual entry errors, and facilitates end-to-end customer journey tracking.
- Enhanced lead nurturing as marketing automation platforms receive real-time CRM insights for personalized outreach.
- Improved inventory management when CRM sales forecasts inform ERP procurement cycles.
- Faster support resolution through synchronized customer histories across CRM and helpdesk tools.
Such integration not only boosts productivity but also empowers teams with comprehensive, up-to-date information, leading to faster, more informed decisions and better customer experiences.
Challenges and Solutions in CRM Analytics Implementation
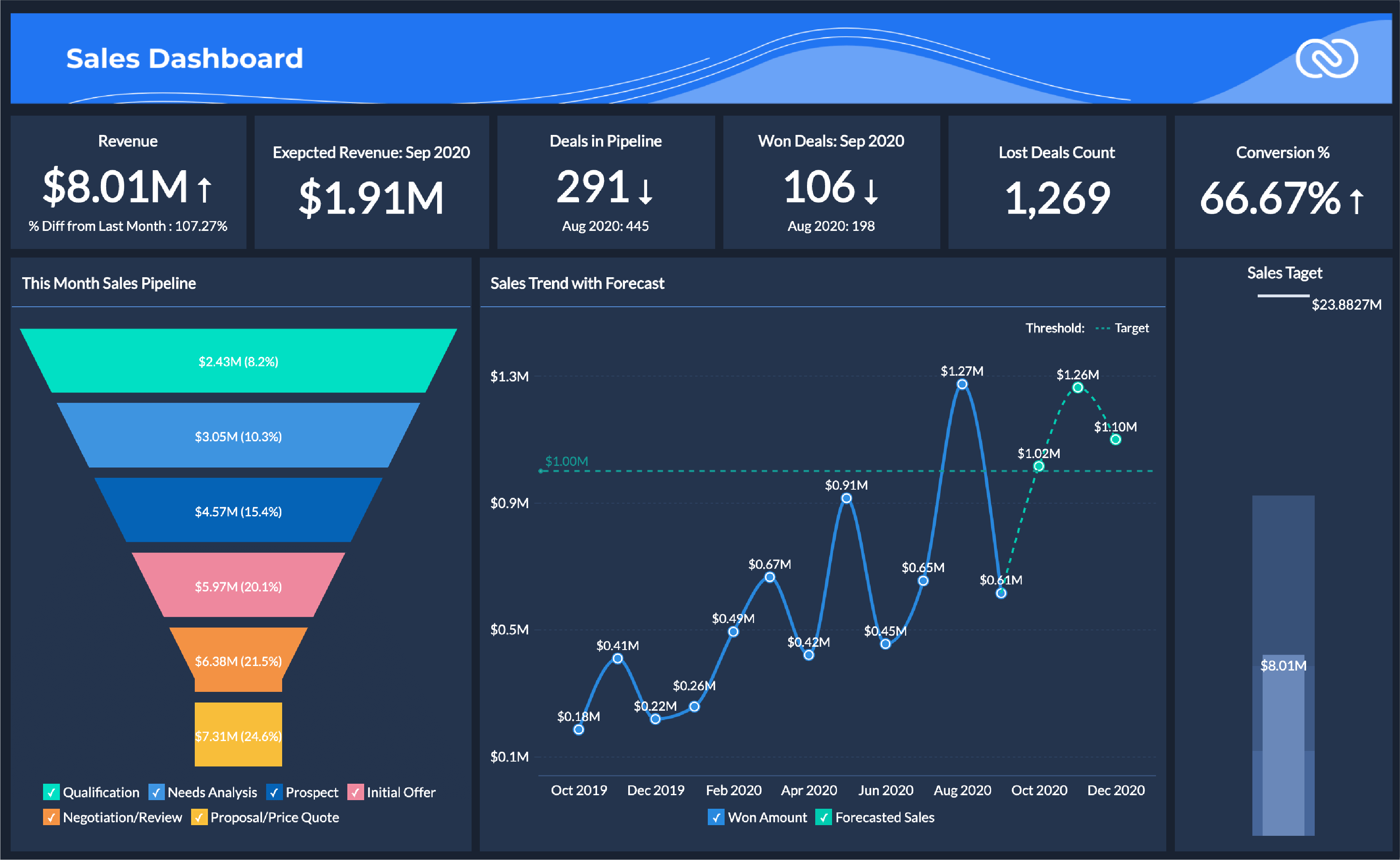
Despite its advantages, implementing CRM analytics poses several challenges for organizations. These obstacles can range from data quality issues to cultural resistance, yet proven solutions and best practices can help ensure successful adoption.
- Ensuring data integrity by establishing robust data governance frameworks and regular audits.
- Integrating disparate data sources using centralized data warehouses or ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes.
- Training staff to build analytical skills and encourage a data-driven culture.
- Safeguarding customer privacy through compliance with regulations like GDPR and implementing strong access controls.
- Choosing scalable analytics platforms that grow with organizational needs.
Maintaining high data quality is essential, as inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misguided decisions. Organizations also need to address privacy concerns by anonymizing sensitive information and enforcing strict data access policies. Regular training and clear communication help overcome resistance, enabling teams to fully embrace CRM analytics initiatives.
Future Trends in CRM Analytics
The landscape of CRM analytics is rapidly evolving, driven by technological innovation and shifting customer expectations. Emerging trends are poised to significantly influence how organizations engage with their customers and derive value from data.
- AI-powered insights for automated customer segmentation, personalized recommendations, and predictive lead scoring.
- Real-time analytics delivering instant feedback on customer interactions and campaign performance.
- Omnichannel data integration merging online, offline, and third-party data for a holistic customer view.
- Voice and sentiment analytics leveraging advancements in natural language processing.
- No-code and low-code analytics platforms democratizing access to data insights across all business functions.
For example, global brands like Amazon and Netflix already harness AI-driven analytics for hyper-personalized experiences. In the future, real-time dashboards will empower teams to adapt strategies on the fly, and integrated omnichannel data will eliminate blind spots in the customer journey. These trends will set new standards for customer engagement, enabling organizations to anticipate needs and exceed expectations with unprecedented accuracy.
Final Summary
In summary, crm analytics examples showcase the dynamic ways businesses can unlock value from customer data, fueling innovation and stronger relationships. As technology evolves, the potential for even deeper, real-time insights only grows, making CRM analytics an essential tool for organizations aiming to stay ahead in a competitive landscape.
Answers to Common Questions
What types of businesses benefit most from CRM analytics examples?
Any business that interacts with customers can benefit, including retail, finance, healthcare, and service industries. The techniques are flexible enough to fit different business sizes and models.
How do crm analytics examples help improve customer retention?
By identifying patterns in customer behavior, CRM analytics enables businesses to create targeted retention strategies and personalized experiences, resulting in higher loyalty and lower churn.
Are crm analytics examples relevant for small businesses?
Yes, many CRM platforms and analytics tools are scaled for small business needs, offering practical insights without requiring large data teams or resources.
What skills are helpful for working with crm analytics examples?
Basic understanding of data analysis, experience with CRM software, and familiarity with data visualization tools are valuable skills for leveraging CRM analytics effectively.
Can crm analytics examples integrate with existing software?
Most modern CRM analytics solutions are designed to integrate with popular business tools like marketing, ERP, and support platforms to unify and streamline data flows.